20 Jul USE OF INDUSTRIAL ROBOTIC ARMS IN AUTOMATING QUALITY CONTROL PROCESS USING NDT METHODS
Manufacturers from different verticals ranging from industrial to aeronautical prefer NDT (Non-Destructive Testing) as their most preferred method of quality control. In the manufacturing industry, testing should be carried out on every final product and its often a rigorous task if you try to accomplish it manually.
Use of robots for NDT finds great application in automating the quality control method in the manufacturing sector. When we try to automate an NDT process, we need advanced scanners and robots to increase the speed and repeatability factor involved in the testing. The quality of scanners and robots are critical in producing precision measurements.
A typical cartesian scanner used for non-destructive testing uses a combination of a linear axis (x,y,z) and a rotational axis. In this article, we will compare a typical cartesian scanner with a robotic arm system that uses up to six polar axes to handle machine tools, welding, and associated movements.
Automated Cartesian Scanners
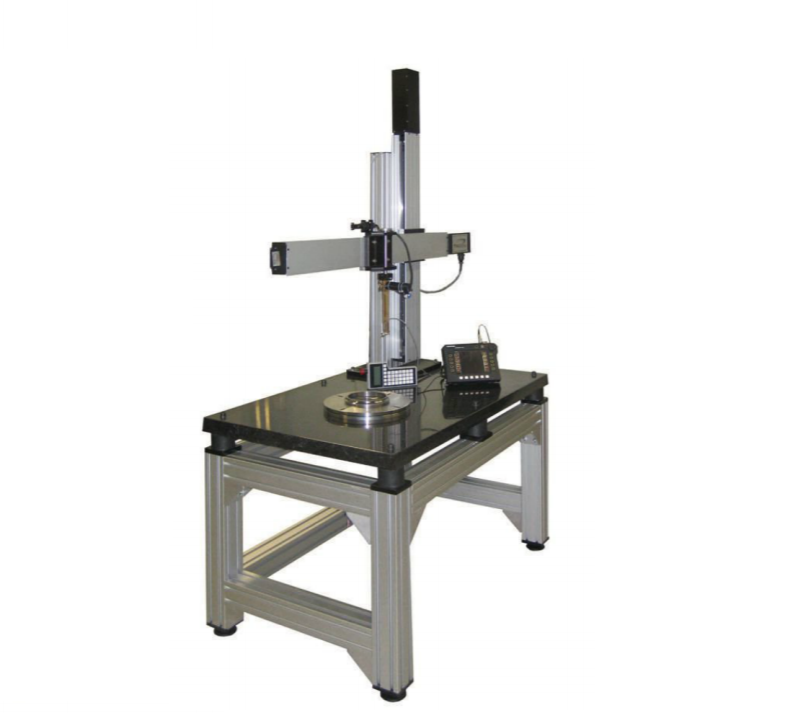

Cartesian scanners used for NDT in industries can be adjusted to match their job specification. A cartesian scanner is an ideal tool for capturing real-time signals while the axes move as they are created using highly precise actuators, stepper motors, and optical encoder modules.
These scanners can be automated with real-time signal processing, repetitive scanning ability, imaging abilities, and high inspection speed. To obtain such capabilities, an automated scanner should have the below features.
- A mechanical design which facilitates high positioning accuracy of all axes.
- A motion control strategy that delivers quick position feedback
- Realtime encoder monitoring
- Very fast data transfer rate
The equipment’s position and stability during signal acquisition are very critical in the result of C-scan mapping. Obtaining such positioning and stability while operating with products that have complex 3d geometries are difficult. Hence an automated Cartesian scanner must be a multi-axis scanner and position of all axes should be synchronized for getting accurate results.
Articulated Arm Robots for high precision scanning

Industrial robotic arms functions very similarly to a human arm. Their precisely articulated mechanical links are linked together to enable rotational motions and handle objects within a volume. Industrial robotic arms are used for various other applications like material handling, welding, laser cutting etc.
A well-articulated robotic arm helps to automate the quality control process in manufacturing units that depends on NDT. Robotic arms provide the cartesian scanning system great dexterity and can add value to advanced NDT methods if they are able to meet the standards of automated NDT testing.
Disclaimer: This video is embedded from the youtube channel FabMetalMag , this is a public video, if the original creators have issue displaying this content in our website please contact us for the removal of the same.
Challenges of Designing Robotic Arms for NDT
Automated NDT systems are the need of the moment for numerous industries in order to increase their productivity. Aerospace industry shows a growing interest in robotic solutions to automate their quality control process using non-destructive testing. However, there are few inspection factors and design challenges that must be taken care of to make robotic designs eligible for automated NDT inspections.
Motion Control Challenges
The traditional motion control designs used by most robotic arms in the industries provides very limited information on the positions of the robotic arm while it is on the move.
A robotic arm used for automated NDT system should be able to collect data while it is moving. So, the motion control system should be able to incorporate extremely fast PID controller loops. When the PID loops close slowly, the arm won’t move in the designed trajectories which can corrupt the NDT signal measurements. Currently available industrial robotic systems offer slow PID loops which is 10 times less than what is required for accurate NDT scanning.
Data Acquisition Speed
It’s very challenging to capture live data while the robotic arm is moving, as its real-time position monitoring is required to achieve this. To enable real-time position monitoring, there should be direct encoder feedback from the robotic system. In traditional robotic systems, position feedback is available only after data is processed by the motion control unit. As NDT automation requires the position to be attached with each measurement point, any delay in getting position feedback will have a direct impact on the speed of the inspection process.
Traditional cartesian scanners can be replaced with an industrial robotic arm and automate the quality control process in the manufacturing industry after we figure out a solution to the above-mentioned challenges. However, as of now, the use of the robotic arm to automate the NDT process is still a work in progress and can benefit the manufacturing industry once it’s successfully implemented.



No Comments